Oracle SCN : System Change Number
System Change Number
SCN is a number generated in the database on the
occurrence of an event in the database, the event could be
- DML statement execution
- SELECT statement execution
- DDL statement
- Commit statement
Whenever this type of transaction happens, the
current timestamp converted into the system change number (SCN)
SCN is useful in MANY DATABASE SCENARIOS SUCH AS
- Instance Recovery
- Roll forward
- Rollback
- Backup and recovery
- Read consistency
SCN is always incrementing because timestamps always
increase.
Snowflake : Undrop database command
Snowflake database has a lot of features and benefits over the
traditional database, one of the features is undrop database, assume you
changed your mind after dropping a database, you can undo it using undrop
database command,
let's see how
exactly it works. this particular feature is based on the time travel feature
of the snowflake, a schema, database or table can be restored within the
parameter value of "data retention period", the default value of the
same is 24 hours or 1 day, and it can set up to 90 days for the enterprise edition.
Undrop feature can be applied
to the table, schema or database, here we will discuss database example
+-----------------------+----------------+----------------+
|
DATABASE_NAME | DATABASE_OWNER |
RETENTION_TIME |
|-----------------------+----------------+----------------|
|
EXERCISE_DB | ACCOUNTADMIN
| 1 |
|
SNOWFLAKE_SAMPLE_DATA | ACCOUNTADMIN |
1 |
|
TECHNODB | ACCOUNTADMIN
| 1 |
+-----------------------+----------------+----------------+
These are the
current databases in the snowflake instance, now I will drop the technodb
snowflake database
technosnow#TECHNO_WS@SNOWFLAKE.INFORMATION_SCHEMA>drop database TECHNODB;
+--------------------------------+
|
status
|
|--------------------------------|
|
TECHNODB successfully dropped. |
+--------------------------------+
1
Row(s) produced. Time Elapsed: 0.610s
technosnow#TECHNO_WS@SNOWFLAKE.INFORMATION_SCHEMA>
technosnow#TECHNO_WS@SNOWFLAKE.INFORMATION_SCHEMA>select
database_name , database_owner, retention_time from databases;
+-----------------------+----------------+----------------+
|
DATABASE_NAME | DATABASE_OWNER |
RETENTION_TIME |
|-----------------------+----------------+----------------|
|
EXERCISE_DB | ACCOUNTADMIN
| 1 |
|
SNOWFLAKE_SAMPLE_DATA | ACCOUNTADMIN |
1 |
+-----------------------+----------------+----------------+
2
Row(s) produced. Time Elapsed: 0.639s
technosnow#TECHNO_WS@SNOWFLAKE.INFORMATION_SCHEMA>
Here I have
dropped a database technodb, you can from the above logs, now we have only two databases
instead of three
technosnow#TECHNO_WS@SNOWFLAKE.INFORMATION_SCHEMA>undrop database TECHNODB;
+------------------------------------------+
|
status
|
|------------------------------------------|
|
Database TECHNODB successfully restored. |
+------------------------------------------+
1
Row(s) produced. Time Elapsed: 0.491s
technosnow#TECHNO_WS@SNOWFLAKE.INFORMATION_SCHEMA>
select
database_name , database_owner, retention_time from databases;
+-----------------------+----------------+----------------+
|
DATABASE_NAME | DATABASE_OWNER |
RETENTION_TIME |
|-----------------------+----------------+----------------|
|
EXERCISE_DB | ACCOUNTADMIN
| 1 |
|
SNOWFLAKE_SAMPLE_DATA | ACCOUNTADMIN |
1 |
|
TECHNODB | ACCOUNTADMIN
| 1 |
+-----------------------+----------------+----------------+
3
Row(s) produced. Time Elapsed: 0.783s
technosnow#TECHNO_WS@SNOWFLAKE.INFORMATION_SCHEMA>
Here we see, that the database has been restored back with the undrop database command, In this way, we
can do it for table and schema as well.
Snowflake : Using snowsql for snowflake database
A snowflake data warehouse
is the latest addition to the trending database technology, In this article, we
will be discussing snowsql, a command line tool used to access the snowflake
database, there is another way as well to access the database i.e. web-based
portal. still, there are many DBA's who love working on the command line
instead of a web-based portal.
Snowsql is supported on the
below platforms
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux or a compatible operating system.
- macOS (64-bit).
- Microsoft Windows (64-bit).
snowsql installer can be
downloaded using the below link
follow the traditional
approach to install snowsql i.e. next, next and finish
once the installation is
complete, execute the below command, if it gives output instead of error then
your snowsql installation is successful
C:\Users>snowsql -v
Version: 1.2.23
C:\Users>
we can see, that snowsql is
installed and the version is 1.2.23
in order to login into the
snowflake database, you need to have an account
name, username, and password
also read know your snowsql account name
PostgreSQL : Types of Shutdown
There are different ways to make a database shutdown for every
database type whether it is MySQL, Oracle, MongoDB, etc, in PostgreSQL as well,
there are 3 types of shutdown based on the signal provided
1.
SIGTERM
2.
SIGINT
3.
SIGQUIT
We will discuss them one by one
SIGTERM
This type of
shutdown is identified as a smart shutdown
After receiving a
shutdown signal, SIGTERM
disallows new connections
let’s existing connection works
normally
shuts down only after sessions
are terminated
If the server is
in online backup mode
It additionally waits
until the online backup mode is no longer active, new connections still are
allowed for superusers only, as they might need to send a request to
disable the are online backup mode
If the server is
in recovery mode
The recovery
process will be stopped only after all regular sessions are terminated.
SIGINT
This mode is
termed fast shutdown mode
once a SIGINT
signal is sent, it
disallows new connections and sends
all existing server processes SIGTERM, which makes them abort respective current
transactions and exit promptly
waits until all server process
to exit and finally shuts down.
if the server is
in online backup mode
the backup mode
will be terminated and the backup will be made useless
SIGQUIT
This mode is
termed immediate shutdown mode
The server will
send SIGQUIT to all the child processes and wait for them to terminate
and if it is not terminated within 5 sec, it sends SIGKILL
After forcing
SIGQUIT,
the database
needs recovery on the next startup
only recommended in case of
emergency.
PostgreSQL : How to check parameter values in postgresql
As part of some basic
administration in PostgreSQL databases, we will learn how to check and modify
parameters
there are a few ways to do it
- using the "Show" command
- querying pg_settings catalog
- by directly checking configuration files
Assume you need to check the
parameter related to the hba_configuration file, like the location of this file
but you are not sure about the parameter name, I just tried with a few
options, and it was not giving me proper value, however, it was throwing syntax
error like below
postgres-# show hba_config;
ERROR: syntax error at or near
"show"
LINE 2: show hba_config;
^
postgres=#
postgres=# show hba;
ERROR: unrecognized
configuration parameter "hba"
postgres=#
for using the "show"
command, you must know the exact name of the parameter, or else you can simply
use pg_settings catalog to fetch it, I just tried the
"like" parameter in pg_settings
postgres=# SELECT name, setting,
reset_val FROM pg_settings where name like '%hba%';
name |
setting
|
reset_val
----------+-------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------
hba_file | C:/Program
Files/PostgreSQL/10/data/pg_hba.conf | C:/Program
Files/PostgreSQL/10/data/pg_hba.conf
(1 row)
now you can check using the "show"
command
postgres=# show hba_file;
hba_file
-------------------------------------------------
C:/Program
Files/PostgreSQL/10/data/pg_hba.conf
(1 row)
postgres=# show max_connections;
max_connections
-----------------
100
(1 row)
PostgreSQL : How to describe table in psql
For the DBA's using a
conventional database such as oracle, they have a habit of using DESC or
DESCRIBE but in PostgreSQL, it's in different ways, we will discuss the same
here
There are 3 ways to describe a table
- using \d
- using \d+
- using view INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS
suppose you want to see the
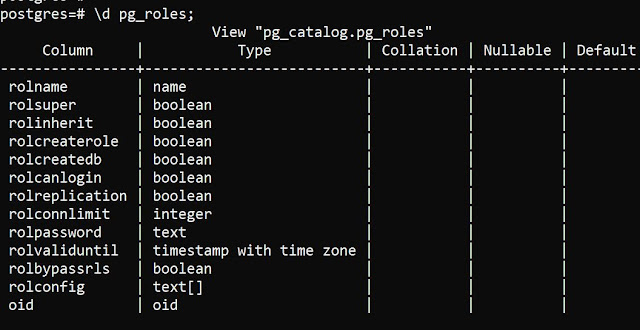
columns in the pg_roles table from the PostgreSQL database
\d will details of columns in
particular table as shown below
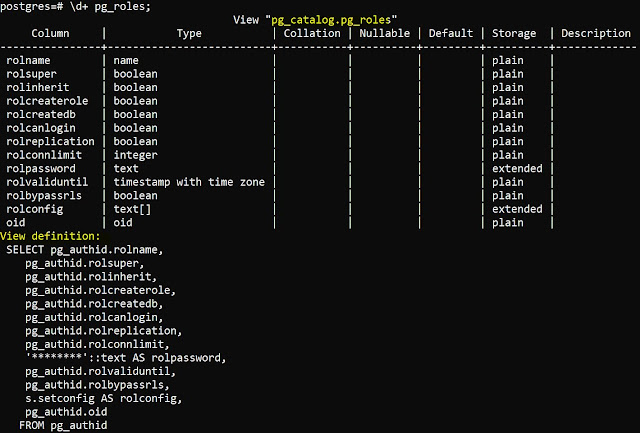
\d+ is an advanced version of \d,
it provides you the definition of the table as well.
You have another way to
describe a table i.e. using SQL query on INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS catalog, there are a number of columns in this table, you can limit what you want to see, select * will give full details, however, I will only select the column name and its data type
select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS;
select column_name, data_type from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where table_name = 'pg_roles';
Oracle : ORA-01017, ORA-02063 preceding line from DATABASE_LINK
Atikh Shaikh
database link, db link, oracle, oracle12c, oracle19c
No comments
![]()
while
creating a database link, I accidentally provided the wrong password of the
remote user and while accessing the database link, it got the below error
SQL>
select * from TECH_AS_OWNER.AS_GARD@asgard_link;
select
* from TECH_AS_OWNER.AS_GARD@asgard_link
*
ERROR
at line 1:
ORA-01017: invalid username/password;
logon denied
ORA-02063: preceding line from
ASGARD_LINK
Error is
quite clear as the password is invalid for a remote account, you have a couple
of options to correct it,
one way
is to drop the existing database link and create it again and the other way is
to alter the database link,
we will
discuss the second option, here i.e., altering the database link.
to alter
the database link, you must have certain privileges as mentioned in the below
table
|
Type of database
link |
Privilege required |
|
Private |
ALTER DATABASE
LINK |
|
Public |
ALTER PUBLIC
DATABASE LINK |
Below are the commands to alter the database link
--grant privilege alter
database link
SQL> grant alter
database link to tech_owner;
SQL> select grantee, privilege from dba_sys_privs where grantee='TECH_OWNER';
GRANTEE PRIVILEGE
------------------------------
----------------------------------------
TECH_OWNER ALTER DATABASE LINK
TECH_OWNER CREATE DATABASE LINK
SQL> ALTER
DATABASE LINK asgard_link
2 CONNECT TO TECH_AS_OWNER IDENTIFIED BY User#123;
Database link
altered.
--verify if database link
is working
SQL> select sysdate from dual@asgard_link;
SYSDATE
---------
29-AUG-22
Similarly we can perform
activity for public database link